
There are many advantages of permanent magnet synchronous motors, which we introduced last time, and this motor is also widely used in agriculture, industry and daily life. So what are the structure and working principles of permanent magnet synchronous motors? Please read the detailed introduction below!
Here’s how it works:
The permanent magnet synchronous motor passes a three-phase current into the stator winding of the motor. After the current is passed, a rotating magnetic field is formed in the stator winding of the motor. Since the permanent magnet is installed on the rotor, the magnetic poles of the permanent magnet are fixed. According to the principle that like magnetic poles attract and opposite poles repel, the rotating magnetic field generated in the stator will drive the rotor to rotate. Eventually, the rotating speed of the rotor will be equal to the rotating speed of the rotating magnetic poles generated in the stator. Therefore, the starting process of this motor can be It is regarded as consisting of an asynchronous start phase and a pull-in synchronization phase.
In the research stage of asynchronous starting, the speed of the motor gradually increases from zero. The main reason for the above is its asynchronous torque, permanent magnet generator braking torque, torque starting reluctance torque and single-axis The rotation is caused by a series of factors such as the asymmetry of the rotor magnetic circuit, so the speed increases with vibration during this process. During the starting process, of the qualitative torques, only asynchronous torque is the driving force, and the motor is accelerated by this torque. Most of the other torques are mainly of braking nature. When the speed of the motor increases from zero to close to the magnetic field rotation speed of the stator, under the influence of the pulsating torque of the permanent magnet, the speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor may exceed the synchronous speed, resulting in a speed overshoot phenomenon. However, after a period of rotational speed vibration, it is finally pulled into synchronization under the effect of synchronous torque.
The structure is as follows:
The permanent magnet synchronous motor is mainly composed of rotor, end cover, stator and other components. Generally speaking, the characteristic of this motor is that its stator structure is very similar to that of an ordinary induction motor. The main difference is that the unique structure of the rotor is different from other motors. The difference from commonly used asynchronous motors is the common structure of the rotor, with high-quality permanent magnet poles placed on the rotor. Since there are many choices for the position of the permanent magnets on the rotor, this motor is generally divided into three categories: built-in, surface-mounted and plug-in, as shown in the figure below. The operating performance of this motor is valued, and there are many factors that affect its performance, but the important one is the structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. In terms of surface mount, plug-in and embedded, each structure has its own advantages.
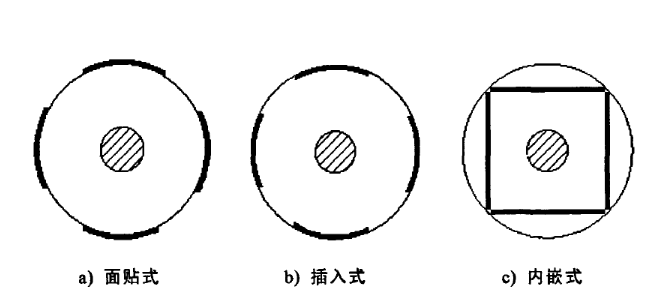
1. Surface-mounted motors are widely used in industry. The primary reason is that they have many advantages that other forms of motors cannot match, such as their convenience in manufacturing, relatively small rotational inertia, and simple structure. Moreover, this type of permanent magnet synchronous motor is easier for designers to optimize its design. The main method is to design the distribution structure of the air gap flux link into a sinusoidal distribution and change its distribution structure to a sinusoidal distribution. It can bring many advantages, such as the negative effects it brings, the ability to reduce the harmonics of the magnetic field, and the use of the above methods can greatly improve the operating performance of the motor.
2. The reason why plug-in structure motors can be compared with surface-mounted motors is that the former is greatly improved because it fully utilizes the magnetic link structure it designed and has asymmetry. The common reluctance torque generated can greatly improve the power density of the motor, and it is also easy to manufacture. Therefore, this structure of the motor is more used in the transmission system, but its shortcomings are also very prominent. For example, the manufacturing cost and magnetic leakage coefficient are much larger than those of the surface mount type.
3. The permanent magnets in the embedded permanent magnet synchronous motor are placed inside the rotor. Although its structure is relatively complex, there are undoubtedly several obvious advantages. Due to its high gas The magnetic flux density of the gap, so compared with the surface-mounted motor, it will produce a large torque; because the installation method of the permanent magnets in the rotor is embedded, so the permanent magnets carry The possibility of a series of risks will be very small, so the motor can run at a higher rotation speed, but there is no need to consider whether the permanent magnets in the rotor will be damaged due to excessive centrifugal force.




















